🌳 Enhancing Orchard Management with Deep Learning
By Mohammadreza Narimani, PhD Candidate at UC Davis
Published: Fall 2024 | Digital Agriculture Laboratory
Introduction
Orchard management is rapidly transforming with the rise of AI-driven analytics, high-resolution imagery, and deep learning. As a PhD Candidate at UC Davis specializing in remote sensing, digital agriculture, and deep learning, I had the privilege of mentoring my undergraduate mentee, Sarbani Kumar, through a full research project in the 2024 UC Davis ESEARCH Program.
Over ten weeks, we developed a cutting-edge workflow using the Geospatial Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) to automatically segment individual orchard trees from NAIP, Google Maps, and WorldView-3 high-resolution imagery. My mentee presented this work at the UC Davis College of Engineering poster showcase, where we were recognized for our contributions to agricultural AI research.
This post summarizes our project, including methods, results, poster, and presentation.
Project Overview
Project Title: Enhancing Orchard Management with Deep Learning: Tree Segmentation Using Geospatial SAM2 Model and Aerial Imagery
Authors: Sarbani Kumar, Mohammadreza Narimani, Ali Moghimi, Alireza Pourreza
Affiliation: Digital Agriculture Laboratory, UC Davis
This project addresses a critical agricultural challenge: accurately identifying and segmenting individual trees in orchards to support yield estimation, biomass calculation, and resource planning.
Using SAM2, an extension of the Segment Anything family optimized for geospatial tasks, we designed a system capable of:
- Precise tree canopy segmentation
- Bounding-box-based tree isolation
- Area calculation for each segmented tree
- Comparison with ground truth labels
- Deployment as an interactive Google Earth Engine tool
Mentoring the Project
Mentoring my undergraduate student on this project involved guiding her through:
- Understanding deep learning architectures (SAM2)
- Processing high-resolution aerial imagery (NAIP, WorldView-3)
- Implementing bounding-box-assisted segmentation
- Ground truth annotation using Label Studio
- Performance evaluation and validation metrics
- Google Earth Engine app development
- Scientific poster design and presentation
- Presenting at UC Davis College of Engineering showcase
My mentee showed exceptional dedication and technical skills, and I am proud to highlight her outstanding work here.

Why Tree Segmentation Matters
Individual tree-level analytics are essential for:
- Yield prediction
- Fruit and nut production estimation
- Canopy health monitoring
- Biomass estimation
- Efficient irrigation and nutrient planning
- Sustainable orchard management
Traditional methods require time-consuming manual labeling. SAM2 dramatically accelerates this process by combining AI, geospatial alignment, and high-resolution imagery.
Methodology Summary
According to the project poster (Fall 2024), our workflow included:
1️⃣ High-Resolution Imagery Acquisition
We used:
- NAIP imagery (<1 m resolution)
- Google aerial tiles
- WorldView-3 imagery (31 cm resolution)
- Limited Maxar satellite samples
This level of detail is crucial for distinguishing trees from shadows and soil.
2️⃣ SAM2 Architecture & Application
The SAM2 pipeline includes:
- Image Encoder
- Memory Attention Module
- Mask Decoder
We optimized SAM2 for orchards by adjusting hyperparameters and creating consistent bounding boxes.
3️⃣ Bounding-Box-Assisted Segmentation
Bounding boxes dramatically improved accuracy:
- Each box contains exactly one tree
- SAM2 focuses solely on one object
- Reduces false positives
- Reduces tree-splitting errors
4️⃣ Ground Truth Validation
Using Label Studio, we manually annotated hundreds of orchard trees for evaluation, ensuring strong visual alignment between model predictions and ground truth.
5️⃣ Area Estimation & Performance Evaluation
We computed area per tree using pixel counts and compared distributions using KDE plots, demonstrating strong modeling accuracy with close alignment between ground truth and SAM2-predicted areas.
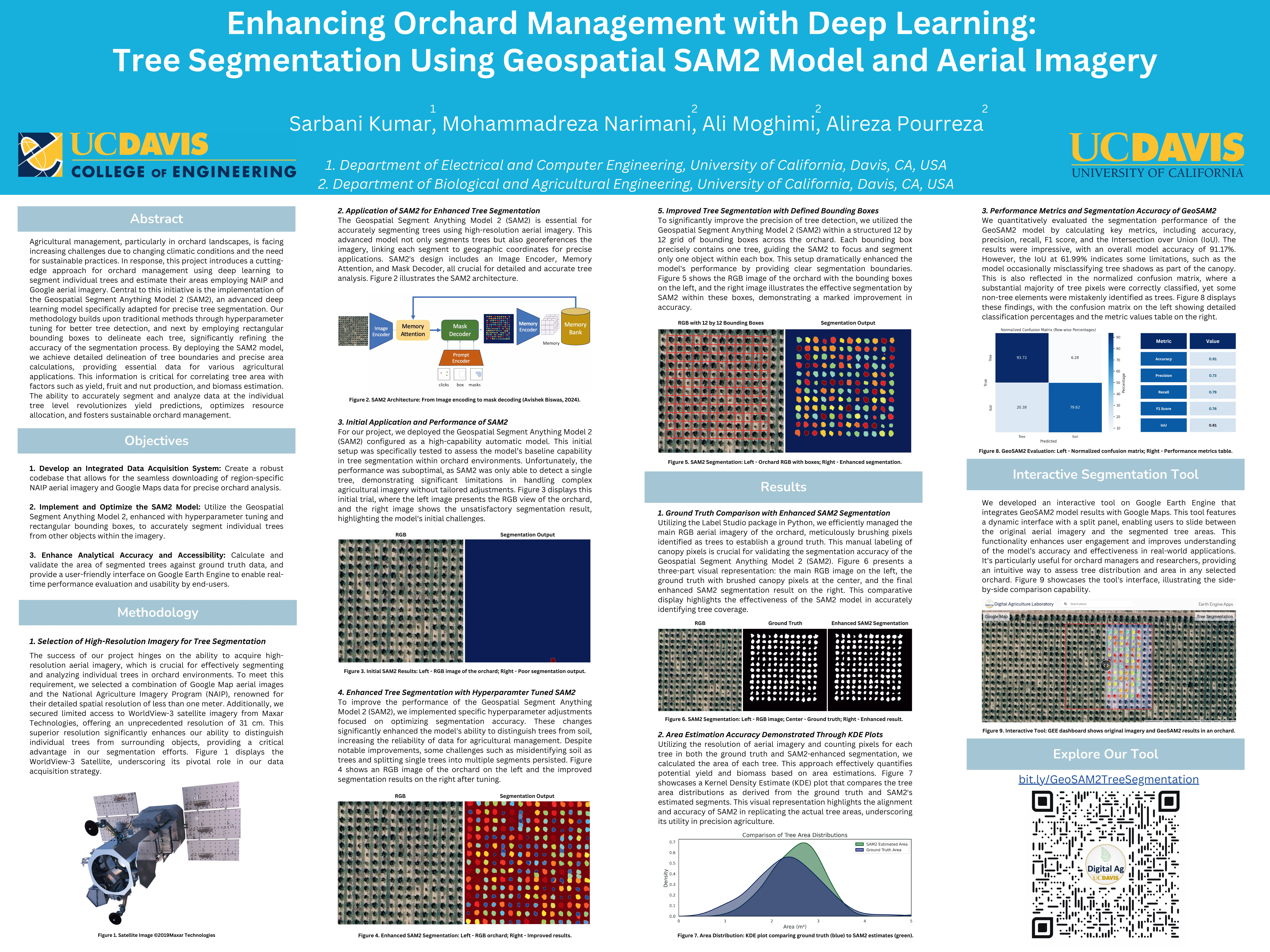
Results
Key outcomes from our research:
- 91.17% overall accuracy
- Excellent precision, recall, and F1 scores
- Strong performance in normalized confusion matrix
- Interactive Google Earth Engine tool for visualization
- SAM2 significantly outperforms baseline methods
- Close alignment between ground truth and predicted tree areas
This fully demonstrates the potential of SAM2 for real-world orchard analytics and precision agriculture applications.
Explore the App & Code
The repository includes:
- NAIP & Google imagery processing scripts
- Python SAM2 segmentation notebook
- Bounding box generation scripts
- Ground truth datasets
- The full research poster
Achievements
At the UC Davis College of Engineering poster presentation, my mentee delivered an excellent overview of our deep-learning workflow and geospatial methods. The project received strong attention from faculty and attendees, recognizing its significance for agricultural automation and environmental AI.
This mentorship experience highlights the mission of the Digital Agriculture Laboratory—empowering students with modern AI, remote sensing, and geospatial tools.
About the Author
Mohammadreza Narimani
PhD Candidate, University of California, Davis
Remote Sensing • AI for Agriculture • Geospatial Deep Learning • Earth Observation
I mentor students in applied machine learning, satellite analytics, Python, and GEE as part of the Digital Agriculture Lab at UC Davis.
📧 mnarimani@ucdavis.edu
🎓 Google Scholar Profile
Conclusion
The GeoSAM2 Tree Segmentation Project demonstrates how high-resolution imagery and advanced deep learning models can revolutionize orchard management. Through this project, my mentee gained real-world experience in AI development, geospatial analysis, and scientific communication.
This work forms the foundation for scalable orchard analytics tools that support smarter farming, better yield predictions, and data-driven resource management.